Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
What is Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)?
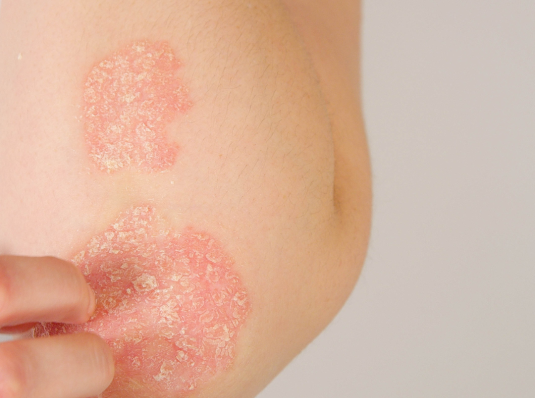
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, itching, redness, and dryness. It can affect people of all ages, though it is more common in children. Eczema often occurs in cycles of flare-ups, followed by periods of remission.
Symptoms of Eczema May Include:
- Itchy, dry, and scaly skin
- Red or inflamed patches, often on the hands, elbows, knees, or face
- Crusting or oozing of affected areas
- Thickened, cracked, or leathery skin over time
Facts About Eczema
- Eczema affects over 31 million Americans, including 1 in 10 children.
- While it is not contagious, eczema is often linked to allergies, asthma, and other immune conditions.
- There is no single cause of eczema, though it can be triggered by irritants, allergens, stress, or changes in weather.
Who is at Risk for Eczema?
Risk factors for eczema may include:
- Genetics: Family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever.
- Age: Eczema is most common in infants and children but can persist into adulthood.
- Sex: Both males and females can develop eczema, though it may present differently in each.
- Other Risk Factors: Environmental irritants, such as soaps, detergents, or allergens, can trigger flare-ups.
How Many Americans Have Eczema?
Approximately 10% of the U.S. population experiences eczema, with varying degrees of severity.
Diagnosis & Management
Eczema is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, patient history, and evaluation of symptoms. In some cases, allergy tests or skin biopsies may be used to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Eczema
Medical and Pharmaceutical Treatments
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and moisturizers are commonly used to reduce inflammation and itchiness.
- Systemic Medications: In severe cases, immunosuppressants or biologics may be prescribed.
- Antihistamines: These can help control itching, especially at night.
Lifestyle Interventions
- Moisturizing Routine: Regular use of emollients helps maintain the skin’s barrier and prevents dryness.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding irritants or allergens is crucial to managing symptoms.
- Stress Management: Stress can worsen eczema, so relaxation techniques or therapy may be helpful.
Have you been diagnosed with eczema?
At Clinical Investigation Specialists, Inc. (CIS Research), we are committed to advancing dermatological care through innovative clinical research. You may be eligible to participate in a clinical trial evaluating new treatments for eczema. For more information on currently enrolling studies, click here.
Resources
Find A Clinical Research Study
CIS does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The content provided is for informational purposes only.
Back To Health Education